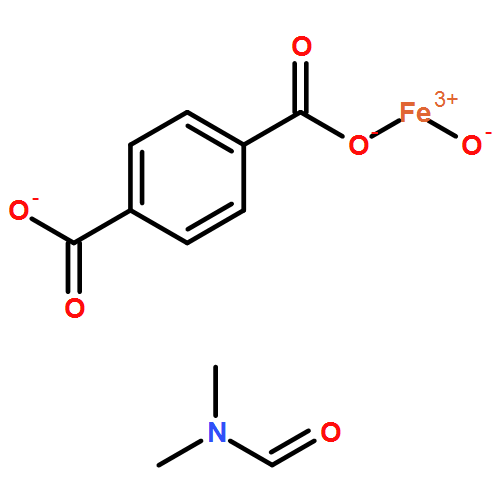
Fe-MIL-68
Fe-MIL-68
CAS:1251849-13-4
M.F.:C8H5FeO5.C3H7NO
M.W.:310.06
Pricing
//
Product: MIL-68(Fe)
Synonyms: Fe(OH)(BDC)·(dmf)x
CAS:1251849-13-4
Basic Information
| Unit MF. | C8H5FeO5.C3H7NO | Unit MW. | 310.06 | ||
| Coordination Metal | Fe | Linkers |
1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (H2BDC) |
||
| Pore Size | Pore Volume | ||||
| Surface Area | 665(10) m²/g (obtained after activation at 300°C for one day) | ||||
| Analog Structure | / | ||||
Product Property
| Appearance | Yellow-brown crystalline needles | |||
| Particle Size | ||||
Stability
1) Thermal stability: Stable up to 300°C in aerobic conditions
2) Thermal decomposition temperature: Above 320°C, the structure collapses to form Fe2O3
2) Thermal decomposition temperature: Above 320°C, the structure collapses to form Fe2O3
Preservation
1) Keep in dry and cool conditions
2) Activation is recommended before use by heating at 300°C under vacuum for one day
Other Features
Redox activity: Suitable as a positive electrode material for lithium-ion batteries, but with relatively low capacity (about 30 mAh/g)
Applications
1) Gas adsorption and separation: Capable of gas adsorption.
2) Energy storage: Can be used as a positive electrode material for lithium-ion batteries
2) Energy storage: Can be used as a positive electrode material for lithium-ion batteries
Characterizations
References
1) Alexandra Fateeva, Patricia Horcajada, Thomas Devic, Christian Serre, Jérôme Marrot, Jean-Marc Grenèche, Mathieu Morcrette, Jean-Marie Tarascon, Guillaume Maurin, Gérard Férey; Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 3789–3794; DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201000486; Synthesis, Structure, Characterization, and Redox Properties of the Porous MIL-68(Fe) Solid